Glaucoma Testing
Many different tests are performed to detect optic nerve damage and vision loss from glaucoma. The most common initial test is the measurement of intraocular pressure (IOP). IOP can be measured through contact and non-contact methods.
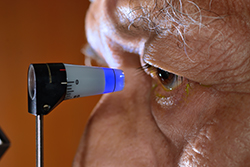
In the contact method, a small, blue-lighted device called a Goldman tonometer is gently pressed on the surface of the eye that has been previously numbed by eye drops. The non-contact method uses a small puff of air to press the eye surface and give a reading of pressure inside the eye.
Visualization of the optic nerve is an important step in determining the health of the eye as well. The doctor looks through a dilated pupil with a special lens and microscope to examine the shape and contour of the optic nerve. A nerve damaged by glaucoma will have a characteristic look, or “cupping,” signifying nerve loss.
Types of Testing
Visual field testing
Visual field testing maps out the actual reception of the optic nerve. It relies on the performance of a patient to see lighted targets and record them by pressing a button. During a visual field test, patients are seated in front of a large, white bowl-shaped machine and are instructed to watch for spots to light up in front them. They push a button every time a white spot is seen. The results are mapped out and printed for the doctor to interpret. Glaucoma has characteristic visual field defects that will appear on this test if the disease is present.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a revolutionary way to detect the presence of glaucoma. During OCT testing, patients will place their eyes in front of a scanner that will map out the nerve layer thickness of the retina and the shape and contour of the optic nerve. Nerve damage from glaucoma will again have characteristic findings on this exam.
Gonioscopy
Gonioscopy is a technique that examines the inner drainage system of the eye. When the aqueous humor drains out of the eye and is replaced by new aqueous, it passes through a specific area called the trabecular meshwork. This meshwork is located in a circular pattern lying at the periphery of the iris. A special contact lens with four mirrors is placed on an anesthetized eye to observe the anatomy of this drainage system. If it is damaged or obstructed, it can cause IOP to be elevated enough to cause glaucoma.
